Biomarkers for precision cancer therapy
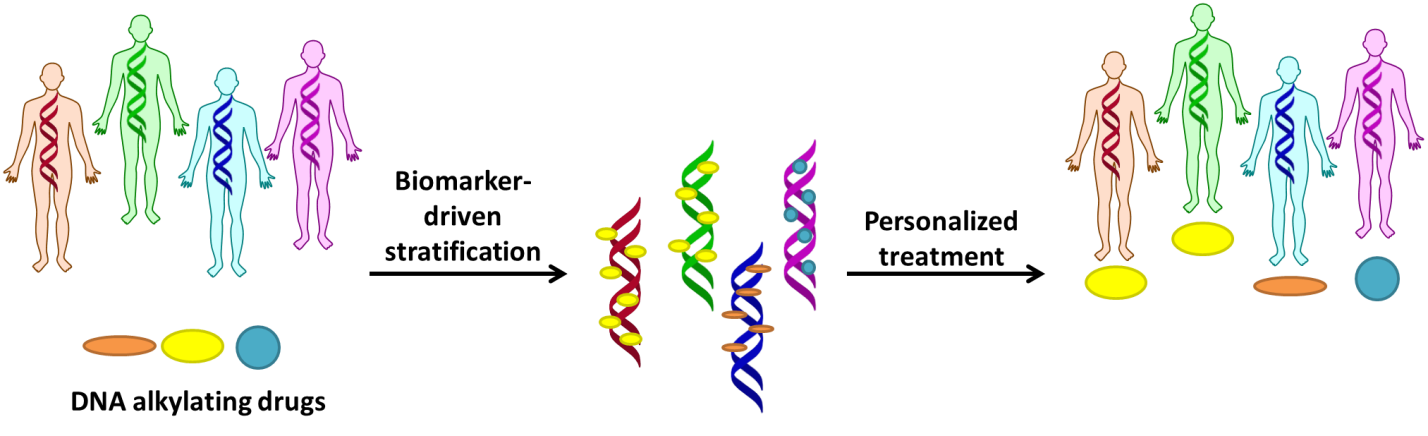
Precision medicine is the emerging therapeutic paradigm involving using individual or population characteristics to select and guide the use of the most effective drugs in a relevant context. A central facet involves quantifying molecular markers in biological samples and generating knowledge concerning how their alterations impact drug efficacy and safety. DNA alkylating anticancer agents are still amongst the most widely and effectively used cancer therapeutics but often suffer from low safety profiles, as well as intrinsic and acquired resistance. We pursue mechanistic investigations concerning DNA alkylating agents centering on how alterations in molecular markers impact drug efficacy, especially for DNA-alkylating pro-drugs that require metabolic activation to generate DNA reactive species. We work to understand factors that impact cytotoxicity, such as transcriptional activation of drug metabolizing enzymes or DNA repair processes. From a practical perspective, this research involves a combination of chemical synthesis, bioanalysis (mainly mass spectrometry), and biochemical studies of isolated enzymes, as well as relating biotransformation capacity, DNA alkylation and cytotoxicity in human cell lines. Aspects of this work concern the mechanistic basis of how combining herbs or bioactive food components with drugs impact efficacy, as well as combination strategies to overcome drug resistance. Finally, we collaborate closely with systems, structural and cancer biologists to characterize systems-wide perturbations of protein networks, understand mechanisms of interactions with DNA-processing enzymes such as RNA and DNA polymerases, and work toward addressing biological models or human biospecimins with translational relevance in cancer therapy.
Literature
Review Articles
Stornetta, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Cimino, G. D.; Henderson, P. T.; Sturla, S. J. DNA adducts from anticancer drugs as candidate predictive markers for precision medicine, Chem. Res. Toxicol, 2017, 30 (1), 388–409. external page DOI
Tanasova, M.; Sturla, S. J. Chemistry and Biology of Acylfulvenes: Sesquiterpene-Derived Antitumor Agents. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6, 3578-3610. DOI
Erzinger, M. M.; Sturla, S. J. Bioreduction-Mediated Food-Drug Interactions: Opportunities for Oncology Nutrition. Chimia, 2011, 65, 411-415. external page DOI
Representative Research Articles
Malvezzi, S.; Farnung, L.; Aloisi, C.; Angelov, T.; Cramer, P.; Sturla, S. J. Mechanism of transcription stalling by DNA alkylation, submitted. DOI
Otto, C.; Spivak, G.; Aloisi, C.; Menigatti, M.; Nägeli, H.; Hanawalt, P. C.; Tanasova, M.; Sturla, S. J. Modulation of cytotoxicity by transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair is independent of the requirement for bioactivation of acylfulvene, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, external page DOI
Stornetta, A.; Villalta, P.; Gossner, F.; Wilson, W.; Balbo, S.; Sturla, S. J. DNA adduct profiles predict in vitro cell viability after treatment with the experimental anticancer prodrug PR104, Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2017, in press. DOI
Malvezzi, S.; Angelov, T.; Sturla, S. J. Minor groove 3-deaza-adenosine analogs: Synthesis and bypass in translesion DNA synthesis, Chem. Eur. J., 2016, external page DOI
Erzinger, M. M.; Bovet, C.; Hecht, K. M.; Senger, S.; Winiker, P.; Sobotzki, N.; Constantinescu, S.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Shay, J. W.; Marra, G.; Wollscheid, B.; Sturla, S. J. Sulforaphane preconditioning sensitizes human colon cancer cells towards the bioreductive anticancer prodrug PR-104A. PLOS One, 2016, external page DOI
Stornetta, A.; Villalta, P. W.; Hecht, S. S.; Sturla, S. J., Balbo, S. Screening for DNA alkylation mono and crosslinked adducts with a comprehensive LC-MS3 adductomic approach. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11706-11713, external page DOI
Malvezzi, S.; Sturla, S. J.; Tanasova, M. Quantification of Pyrophosphate as a Universal Approach to Determine Polymerase Activity and Assay Translesion Synthesis Inhibitors, Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 1-7. external page DOI
Erzinger, M. M.; Bovet, C.; Uzozie, A.; Sturla, S. J. Induction of Complementary Function Reductase Enzymes in Colon Cancer Cells by Dithiole-3-Thione vs. Sodium Selenite, J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 29, 2015, 10-20. external page DOI
Constantinescu, S.; Hecht, K.; Sobotzki, N.; Erzinger, M. M.; Bovet, C.; Shay, J. W.; Wollscheid, B.; Sturla, S. J.; Marra G.; Beerenwinkel, N. Transcriptomic responses of cancerous and noncancerous human colon cells to sulforaphane and selenium. 2014, Chem Res. Toxicol. 27, 377-386. external page DOI
VanMidwoud, P.; Sturla, S. J. Improved efficacy of acylfulvene in colon cancer cells when combined with a nuclear excision repair inhibitor. 2013. Chem Res. Toxicol. 26, 1674-1682. external page DOI
Tanasova, M.; Plutschack, M.; Muroski, M. E.; Sturla, S. J.; Storuse, G. F.; McQuade, D. T.; Fluorescent THF-Based Fructose Analogue Exhibits Fructose-Dependent Uptake. 2013, Chembiochem, 14, 1263-1270. external page DOI
Pietsch, K. E.; van Midwoud, P. M.; Villalta, P. W.; Sturla, S. J. Quantification of acylfulvene- and illudin S-DNA adducts in cells with variable bioactivation capacities. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 146–155. external page DOI

