Food-Drug Interactions
The LFNT is part of a multi-group team from the ETH Zurich and the University of Zürich supported by a SINERGIA grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation. The team studies the impact of bioactive food components on enzyme regulation, protein expression, and drug metabolism, with the goal of developing methods for predicting cancer drug efficacy in individuals.
Impact of Bioactive Food Components on Enzymes and Metabolism
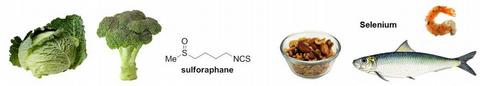
The expression and function of reductase enzymes influence the susceptibility of human cells to electrophilic chemicals, including toxicants and drugs. Common components of the diet, such as sulforaphane (derived from cruciferous vegetables) and selenium (found in Brazil nuts, fish, shrimp, and meat) can activate the transcription of reductase enzymes. Furthermore, reductive enzymes are also overexpressed in certain tumor cell lines. A focus of this research is to understand how bioactive food components effect anticancer drug efficacy.
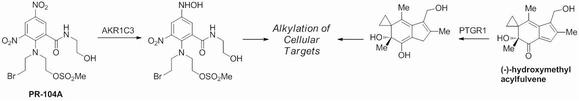
Reductive enzymes such as alkenal/one oxidoreductase (AOR, also known as PTGR1) or aldo-keto reductase 1 C3 (AKR1C3) can catalyze the bioactivation of drug molecules like PR104A or hydroxymethyl acylfulvene. The activated intermediates alkylate cellular nucleophiles like DNA and proteins, which can induce apoptosis.
Contributions of the Laboratory of Food and Nutrition Toxicology to this field of research include:
- evaluation of the impact of food components in modulating metabolism and drug toxicity in vitro.
- identification and quantification of DNA adducts with mass spectrometry based analytical methods.
- evaluation of transcription-coupled nuclear excision repair of DNA adducts.
Previous research in our lab centered on the DNA-alkylating drug acylfulvene has demonstrated how reductive bioactivation may be exploited for inducing selective toxicity in cancer cells. For more information, see the external page comprehensive review article published by Tanasova and Sturla.
Collaborators:
FNSNF
UZH

