Mechanisms of Mutagenesis
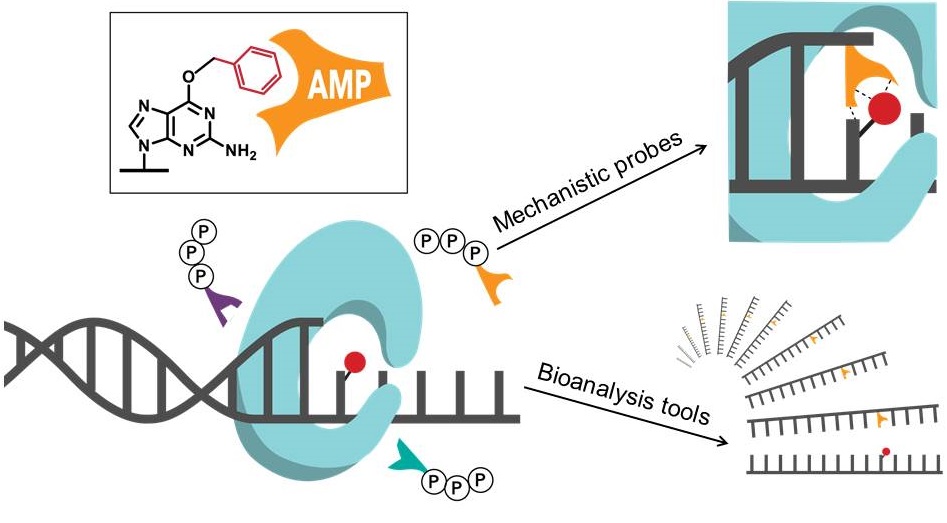
The influence of diet and environment on human cancer etiology arises from acquired mutations in critical growth-regulating genes. The interaction of chemical exposures and metabolic processes leads to the generation of potent chemical alkylating agents in cells that damage DNA and form DNA adducts in the genome. However, the great complexity of relationships between the chemistry of DNA alkylation and the biological consequences of carcinogenesis has limited prediction of cancer risk. Our research aims to understand chemical and biochemical factors that influence replication fidelity and create new tools for genome-wide mapping of chemical-induced base modification. We have advanced the use of a new class of synthetic nucleotides as adduct-directed nucleoside probes and used these and other chemistry-based approaches to address mechanisms of mutations and enable the first replication of alkylated DNA, incorporating a synthetic nucleotide as a marker for positions of DNA damage.
News of our results
Johnson, Madeleine. New Method Pairs Artificial Nucleotide, Mutant Polymerase to Detect DNA Adducts. Genomeweb, 21.1.2015 DOI
Damaged DNA Amplified, Analytica World, 20.1.2015 external page DOI
Bergamin, Fabio. Damaged DNA Amplified. ETH News, 15.1.2015 DOI
Representative Publications
Geigle, S. N.; Wyss, L. A.; Sturla, S. J.; Gillingham, D. G. Copper carbenes alkylate guanine chemoselectively through a substrate directed reaction. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8 (1) 499-506. DOI
Räz, M. H.; Dexter, H. R.; Millington, C. L.; van Loon, B.; Williams, D. M.; Sturla, S. J. Bypass of mutagenic O6-Carboxymethylguanine DNA Adducts by Human Y- and B-Family Polymerases. Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2016, 29 (9), 1493-1503. DOI
Trantakis IA, Nilforoushan A, Dahlmann HA, Stäuble CK, Sturla SJ. In-Gene Quantification of O6-Methylguanine with Elongated Nucleoside Analogues on Gold Nanoprobes. J Am Chem Soc., 2016, 138 (27), 8497-8504. DOI
Wyss, L.; Nilforoushan, A.; Williams, D. M.; Marx, A.; Sturla, S. J. The use of an artificial nucleotide for polymerase-based recognition of carcinogenic O6-alkylguanine DNA adducts, Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44 (14), 6564-6573. DOI
Crespan, E.; Furrer, A.; Rösinger, M.; Bertoletti, F.; Mentegari, E.; Chiapparini, G.; Imhof, R.; Ziegler, N.; Sturla, S. J.; Hübscher, U.; van Loon, B.; Maga, G. Impact of ribonucleotide incorporation by DNA polymerases β and λ on oxidative base excision repair. Nature Comm. 2016 Feb 26;7:10805. external page DOI
Wyss, L. A.; Eichenseher, F.; Suter, U.; Nilforoushan, A.; Blatter, N.; Marx, A.; Sturla, S. J. Specific incorporation of an artificial nucleotide opposite a mutagenic DNA adduct by a DNA polymerase, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 30-33. DOI
Trantakis, I.; Sturla, S. J. Gold Nanoprobes for Detecting DNA Adducts, 2014, Chem. Comm. 50, 15517-20. DOI
Gahlon, H. A.; Boby, M.; Sturla, S.J. O6-alkylguanine postlesion DNA synthesis is correct with the right complement of hydrogen bonding, 2014, ACS Chem. Biol. 9, 2807-14. DOI
Kowal, E.A., Lad, R., Pallan, P.S., Dhummakupt, E., Wawrzak, Z., Egli, M., Sturla, S., & Stone, M.P. Recognition of O6-Benzyl-2'-deoxyguanosine by a Perimidinone-Derived Synthetic Nucleoside: An Interstrand Stacking Interaction. Nucl. Acids Res. 2013, 41, 7566-7576. external page DOI
Gahlon, H. L.; Schweizer, B. W.; Sturla, S. J. Tolerance of Base Pair Size and Shape in Postlesion DNA Synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6384–6387. DOI
Gong, J.; Sturla, S. J. A Synthetic Nucleoside Probe that Discerns a DNA Adduct from Unmodified DNA. J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 4882-4883. DOI
